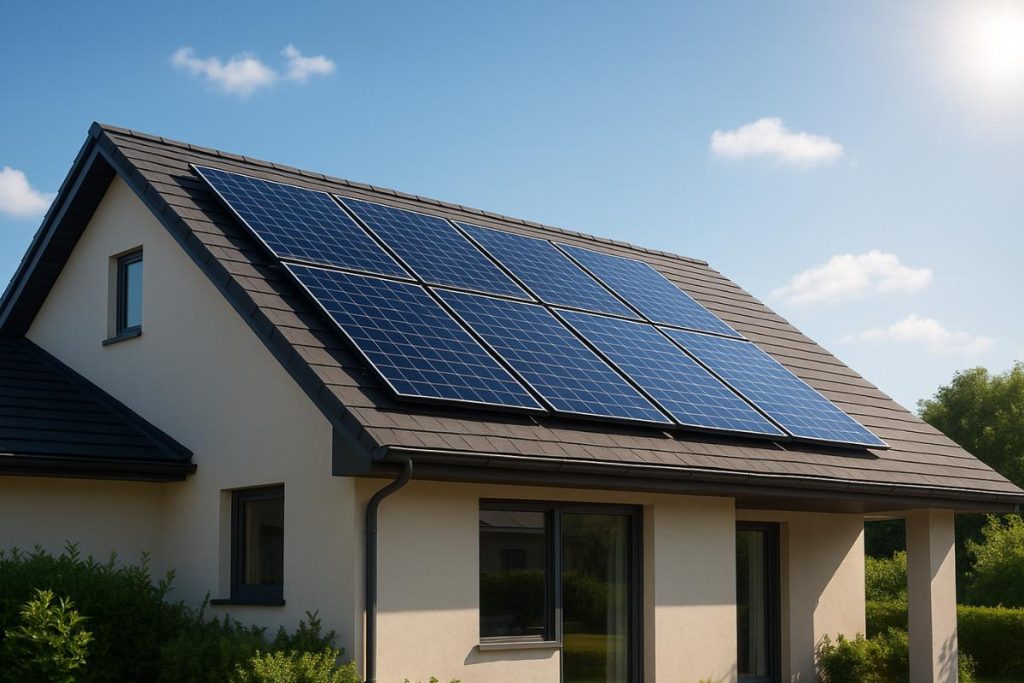
The photovoltaic solar panelalso called solar panel or photovoltaic moduleis a device capable of converting sunlight into electricity. These plates are made up of several solar cells made of semiconductor material (usually silicon) which, when exposed to sunlight, generate electricity through the photovoltaic effect. The energy produced is clean and renewableThis helps to reduce electricity bill costs and reduce the environmental impact compared to traditional energy sources.
In recent years, solar panels have gained prominence in Brazil due to the search for sustainability and economy. Whether on residential roofs, businesses or large solar power plants, these panels make it possible to harness the abundant energy from the sun to generate electricity locally.
In this complete guide, you will understand in detail what a solar panel is and how it worksThe main types and technologies available are how much energy a solar panel generatesaverage values of price and return on investment, as well as discovering the advantages of using solar energy in your property. At the end, we answer the most frequently asked questions and show you how you can take the next step towards installing your solar panels safely.
What is a photovoltaic solar panel?
A photovoltaic solar panel is the central component of a solar energy system. It is a panel made up of interconnected photovoltaic cells, encapsulated between protective layers (glass on the front and an insulating material on the back) and surrounded by an aluminum frame. Its function is to capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect, a physical phenomenon in which light energy releases electrons in the semiconductor material of the cell, generating an electric current.
Each solar panel usually has tens or hundreds of photovoltaic cells crystalline silicon. The cells are joined in series and parallel to achieve the desired voltage and current of the module. A layer of tempered glass on the front protects the cells from rain, hail and dirt, allowing light to pass through. The aluminum frame provides structural rigidity and makes installation easier, while a junction box the back houses the electrical connections and bypass diodes (which help the panel to continue generating even if some part is shaded). In short, the solar panel is built to be weather-resistant and last for decades generating energy, as long as it is well installed and maintained.
Main components of a solar panel
- Photovoltaic cells: small semiconductor sheets (usually monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon) that convert light into electricity. They are the "heart" of the panel.
- Tempered glass: transparent front layer that protects the cells from impacts and moisture, while letting sunlight through.
- EVA and backsheet: layers of plastic encapsulation that seal the cells, guaranteeing electrical insulation and protection against infiltration.
- Aluminum frame: structure around the panel that provides mechanical support and facilitates fixing to roofs or supports.
- Junction box: module on the back where the output terminals (positive and negative cables) and diodes for current management are located, allowing the panel to be securely connected to the system.
How are solar panels manufactured? In a nutshell, manufacturing involves several steps to assemble and protect the photovoltaic cells inside the panel. Typical steps include:
- Glass preparation: cleaning and positioning a tempered glass panel that will serve as the front for the panel.
- Cell positioning: the solar cells are arranged in series/columns on the glass, forming a matrix, and interconnected by thin silver conductive strips (bus bars).
- Lamination: an EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate) film is applied to the cells and a backsheet movie on the back, forming a sandwich. The whole assembly goes through a vacuum and heat lamination, which seals the layers and prevents air or moisture from entering.
- Installation of the junction box: is fixed behind the panel, connecting the conductive strips from the cell terminals to the output electrical cables, including the bypass diodes.
- Frame and finish: the resulting laminate is framed with aluminum profiles at the edges, ensuring rigidity. The panel then undergoes quality inspection and electrical generation tests.
- Packaging: the finished solar panels are packed and palletized for transportation and for lifting solar panelsThey arrive at the consumer ready for installation.
This advanced manufacturing process results in a robust product, capable of operating under sun, rain and temperature variations for more than 25 years. Production technology has evolved to increase the efficiency of the cells and the durability of the plates, making solar energy increasingly accessible and reliable.
How does a solar panel work?
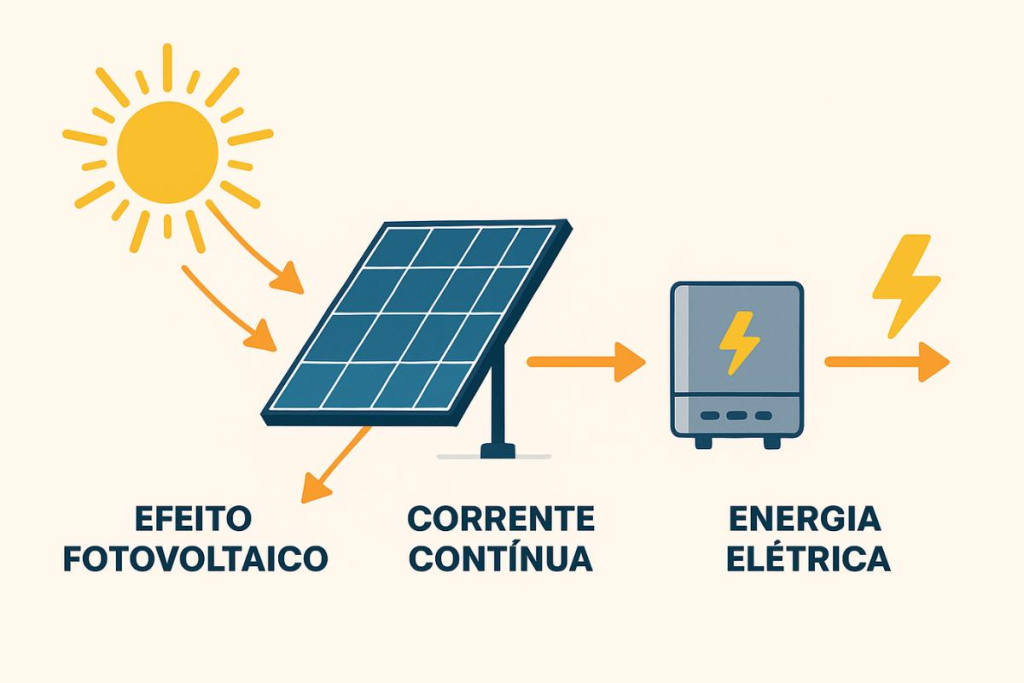
O solar panel operation is based on the photovoltaic effect, discovered in the 19th century, which occurs in semiconductor materials when they are exposed to light. Each cell on the board has a PN (positive and negative layers of silicon doped with impurities). When sunlight (photons) falls on the cell, the photons transfer energy to electrons of the semiconductor material. These electrons gain enough energy to free themselves from their atoms, creating a flow of electrical charges, in other words a direct electric current (DC) circulating through the cell's contacts.
The individual cells generate a relatively low voltage (around 0.5V each). When they are interconnected inside the solar panel, they add up their voltages to reach useful values (a typical 36-cell panel generates ~18V in open circuit, a 60-cell panel ~36V, etc.). The board cables then supply this energy in direct current to the external system.
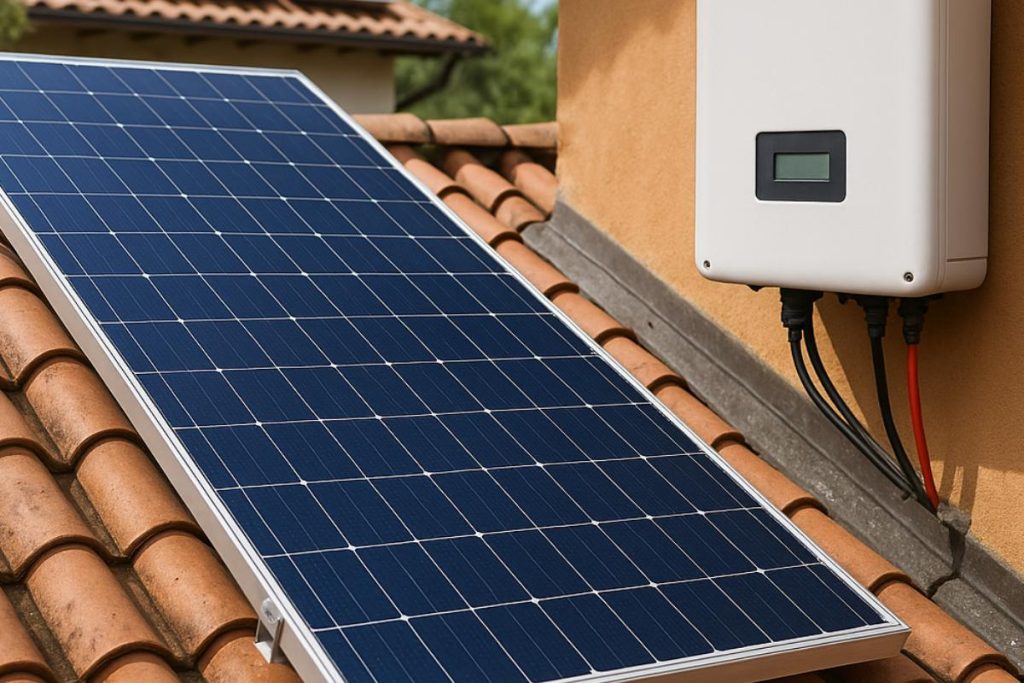
It is important to note that the electricity generated by the plates is direct current (DC)while most appliances and the electricity grid use alternating current (AC). For this reason, in systems connected to the grid (on-grid), equipment called solar inverterThe inverter converts energy from DC to AC synchronized to the grid, allowing immediate use in the home or injection of the surplus into the distribution grid. In isolated systems (off-grid) with batteries, the inverter is also used to supply AC to local equipment from the batteries.
Thus, sunlight activates the photovoltaic cells, generating direct current; this current is collected and converted by the inverter into usable alternating current. The whole process is silent, sustainable and pollution-freeIt is an inexhaustible source of energy (the sun). As long as there is light shining on the plate (even on cloudy days, even if only slightly), it will be producing electricity.
What are the types of solar panels?
There are different types of photovoltaic solar panels available, which vary in terms of cell technology, manufacturing material and module design. The main categories include:
Monocrystalline silicon
Plates made up of silicon cells formed from a single continuous crystal. They have a uniform dark color and are the more efficient between traditional commercial technologies (efficiency rates in the range of 18% to 22% or more). Due to their higher efficiency, they generate more energy in the same area, making them ideal when space is limited (e.g. small roofs). They tend to cost a little more per watt, but offer excellent performance and durability.
Polycrystalline silicon
They use silicon cells made up of multiple crystals (visible as bluish grains in the cell). They are less efficient than monocrystalline (around 16% to 18% typical efficiency), but they tend to be a little cheaper. They were very popular in previous years due to their better cost-benefit ratio, but today mono panels dominate the market as the price difference has narrowed. Even so, poly panels can be advantageous in projects where space is not an issue and you are looking to reduce initial costs.
Thin Film
They encompass various technologies that do not use conventional crystalline silicon cells. Examples: amorphous silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe) e CIGS (copper indium gallium selenium). These sheets have cells deposited in very thin layers on glass or plastic, resulting in lighter and sometimes flexible panels. In general, they are less efficient (10% to 14%) and degrade more quickly, but they can be useful in specific applications such as façades, lightweight calculation or architectural integration. In the residential market, they are not very common in Brazil.
Bifacial
It is worth highlighting one panel type which can be manufactured with mono silicon or other technologies, but with a special feature: generation on both sides. The bifacial plates have glass on both the front and back, allowing photovoltaic cells to receive direct sunlight on the front face and also light reflected from the ground on the back face. This can increase generation by solar power plants on the ground or on light surfaceswhere reflected light (albedo) contributes significantly.
For residential use on conventional roofs (which do not reflect light), the gain is small. Bifacial plates are usually used in large-scale projects or structures such as carports and parking lot covers, where they can generate up to ~10-20% more energy than a similar monofacial panel under the right conditions.
Advanced technologies
he photovoltaic industry is constantly innovating. Some modern panels incorporate technologies such as PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell), TOPCon (Tunnel Oxide Passivated Contact) e HJT (Heterojunction) in the cells, which can increase efficiency and performance compared to traditional cells. For example, PERC and TOPCon cells have extra layers that reduce electron recombination, making better use of incident light. HJT cells, on the other hand, combine crystalline silicon with layers of amorphous silicon, achieving even greater efficiency and better performance at high temperatures.
There is also research on perovskite e tandem cells (which combine two types of material) to break efficiency limits in the future. These innovations are already reaching the market in modules from leading manufacturers, including BYD, making the boards more efficient, durable and aesthetically enhanced (e.g. designs busbarless without apparent busbars on the front, to maximize the active area and improve the appearance of the panel).
Which type to choose? In practice, for residential and commercial projects, the monofacial monocrystalline silicon panels are currently the most widely used, as they offer high performance and reliability. Polycrystalline plates still work well, but are falling out of favor. On the other hand, bifacial panels with cutting-edge technologies are interesting for getting every extra drop of energy when the budget allows or for specific projects. The important thing is to match the type of board to your needs: consider the space available, the local climate (modern panels tend to perform better in hot regions due to improved temperature coefficients), and of course, the cost-benefit ratio of each option.
How much energy does a solar panel generate?
A energy generated by a solar panel depends on several factors: panel powerthe amount of sun it receives per day (local solar irradiation), the angle of inclination and any shading. Panels are sold with a nominal power in watts-peak (Wp), measured under standard test conditions. In practice, each 1 kW of panels installed can produce between ~100 kWh and 150 kWh of electricity per month, depending on the region of Brazil and the season.
For example, an ordinary photovoltaic panel today has a power of around 500 Wp. In a location with good sunshine (North/Northeast Brazil), a single 550 W panel can generate around 60 kWh per month. In regions with lower solar incidence (such as the South of the country), this monthly generation can be around 45-50 kWh per month per panel. For smaller panels, the calculation is proportional: a 100 W panel would generate approximately 12 to 20 kWh/month, taking into account system losses.
It is important to note that systems connected to the grid have some lossesPart of the energy is dissipated in the cables, inverters and components, as well as any shadows or dirt on the modules. Generally, a loss of 10% to 20% is considered between the theoretical power and the energy actually used at the inverter's output. Even so, solar panels are becoming more efficient every year, and with good sizing it is possible to supply a large part (or all) of a home's electricity consumption with just the photovoltaic energy generated on your own roof.
Practical example: Imagine a house that consumes 300 kWh per month. In a region with average sunshine, a photovoltaic system with an installed power of around 2.5 kWp to 3 kWp would be needed to generate this amount. This corresponds to approximately 5 or 6 500 W solar panels each, occupying an area of 10 to 12 m² on the roof. In sunny regions, 4 to 5 panels may be enough; in less sunny areas, 6 or 7 panels may be needed for the same generation.
For this reason, the number of panels required varies according to location and consumption: a solar designer will carry out this analysis, taking into account the solar radiation data for your city to define the exact number of modules to supply your energy use.
How much does a solar panel cost?

O price of a photovoltaic solar panel can vary according to their power, technology and manufacturer. In the Brazilian market, solar panels for residential/commercial use (between 400 Wp and 600 Wp of power) cost on average from R$500 to R$1,000 per unit in retail stores. This figure usually includes tax and can be lower when buying in quantity for a complete system. For example, a 450 W board from a well-known brand can cost around R$600-800, while a state-of-the-art 550 W module can come in at around R$900 - 1,000.
Factors that influence the price of a solar panel:
- Power and efficiency: higher wattage and higher efficiency boards (e.g. 550W with 21% efficiency) tend to cost more than 330W boards with 17% efficiency, because they deliver more power in the same size.
- Technology: modules with new technologies (half-cell, PERC, TOPCon, bifacial) usually cost a little more because they bring performance gains.
- Brand and guarantee: Internationally or nationally renowned manufacturers, who offer robust warranties (10-12 years product, 25 years performance), can command a slightly higher price for quality and support. Established brands also undergo rigorous testing and certification (INMETRO, IEC), adding confidence to the product.
- Quantity and distribution: buy complete kits or wholesale volume can reduce the unit price. In addition, prices vary according to the distributor/region and any promotions or subsidies available.
You can also find mini solar panels for much lower prices. For example, small 5W, 10W modules (used to charge batteries for specific use or teaching projects) can cost between R$30 and R$100. However, these small panels are not suitable for generating significant energy in homes - they are only suitable for applications such as pumping water in remote locations, lighting small LED lights, charging phones when camping, etc. To supply a home or business, the ideal is to invest in regular-sized photovoltaic panels (usually 1.7 m² each) connected to a system with an inverter and other equipment.
Total system investment: Remember that the cost of the solar panel is only part of the investment in solar energy. A complete photovoltaic system includes, in addition to the modules, the inverter, mounting structures, cabling, electrical protections and installation labor. On average, the price of an installed system is between R$4 to R$6 per watt (in 2025), which means approximately R$20 thousand to R$30 thousand for a 5 kWp system serving an average household. This figure may seem high at first, but the good news is that the return comes in the form of savings on the electricity bill: typically, a system pays for itself in 4 to 6 yearsAnd as the useful life exceeds 25 years, all the rest is profit and practically free energy. There are also lines of financing and incentives which make it easier to purchase. In other words, the cost of the panel itself is affordable and has been falling year on year, making solar energy one of the most popular. cheaper forms of generation in the long term.
How efficient is a solar panel?
A efficiency of a solar panel indicates the fraction of the sun's light energy that the panel is able to convert into usable electrical energy. It is expressed as a percentage (%). For example, a panel with 20% efficiency converts 20% of the incident solar radiation into electricity, dissipating the rest in the form of heat or other losses. Typical efficiencies vary depending on the panel technology:
- Plates modern monocrystalline~18% to 22% average efficiency (some models get close to 23-24%).
- Plates polycrystalline~15% to 18% efficiency.
- Technology thin film10% to 14% (some amorphous variations are even less than 10%).
- New technologies (TOPCon, HJT, tandem perovskite + silicon): they have already reached 25% to 30% in the laboratory, but commercially they are in the high 20-23% range.
Efficiency is important because it determines how much energy can be generated per square meter of panel. A 20% efficient panel will generate twice as much energy as a 10% panel occupying the same area under the same sunny conditions. For the consumer, this mainly influences required roof areaIf you have limited space, choosing more efficient boards allows you to install more power in the same amount of space. On the other hand, if there is plenty of space, slightly less efficient (but cheaper) boards can meet demand by occupying a few more square meters.
It is worth noting that the nominal efficiency is measured under standard conditions (irradiation of 1000 W/m², cell temperature at 25°C, etc.). In reality, factors such as high temperatures and dirt can reduce instant efficiency somewhat. Solar panels work best in mild temperatures; on very hot days, the efficiency of the cells drops by a few percentage points due to heating (a common effect with semiconductors). For this reason, ventilating the panels and installing them at the right angle helps to maintain performance.
When planning a photovoltaic system, professionals take into account the efficiency of the panels and the local irradiance to estimate generation. A good installation, oriented to the geographic north (in Brazil) and with an adequate inclination, will ensure that the plates receive as much light as possible throughout the year, making the most of efficiency energy conversion of its modules.
What is the ideal direction and inclination of the solar panels?
A best orientation for installing solar panels in Brazil is aimed at the NorthThis ensures the greatest exposure to the sun throughout the day. As we are in the southern hemisphere, north-facing surfaces receive more direct solar irradiance. In addition to the horizontal direction (azimuth), the angle of inclination in relation to the ground is also important: the ideal is usually close to the horizontal direction (azimuth). local latitude. For example, in Salvador (latitude ~12°S), panels inclined at around 12 degrees work well; in Porto Alegre (latitude ~30°S), inclinations of around 25° to 30° are recommended. This inclination optimizes the capture of sunlight throughout the year, compensating for the differences between summer and winter.
In practice, sloping roofs already provide a good angle, and installers adjust structures to optimize the position. On flat roofs or on the ground, support structures with the right inclination are used. The azimuth is also assessed: if the roof faces east or west, the tiles can be installed on these faces, but they will produce slightly less than if they faced north. Orientations to the south should be avoided as much as possible, as there is a significant loss of generation.
In addition to position, another critical factor is avoid shadingShading from trees, water tanks, walls or other obstructions can drastically reduce the energy generated, as shaded cells act as bottlenecks in the panel's current. A good solar project provides for spacing and positioning that minimizes shadows throughout the day and year. In some cases, optimizers or microinverters are used to mitigate the effect of partial shadows, but the best solution is to plan the installation in a location with full solar incidence during peak sunlight hours (typically from 9am to 3pm).
How many solar panels do I need?
The number of solar panels required to meet a given energy consumption will depend on the monthly electricity consumption location and average production per plate in that region. As we have seen, a ~550 W panel can generate around 50 to 60 kWh per month under favorable conditions. Therefore, to supply 100% of consumption, we make a simple calculation: divide the monthly consumption by the monthly generation per panel.
For example: if a house spends 300 kWh/month and each 550 W panel generates ~55 kWh/month, it would take about 6 solar panels (300 / 55 ≈ 5.5, rounded up to 6 units). A smaller home consuming 150 kWh/month, on the other hand, could be supplied with 3 550 W panels (since 3 x 55 = 165 kWh, covering a safety gap). On the other hand, a farm or business consuming 1,000 kWh/month would require around 18 to 20 panels of this size.
However, there are important regional differences: in the North/Northeast, where insolation is higher, each plate yields more kWh/monthIf you are using a solar panel, you may need one less unit compared to the South for the same consumption. For this reason, professionals use software with irradiance data to calculate sizing precisely. In addition to current consumption, consideration is given to whether demand may increase in the future (purchase of new appliances, air-conditioning, electric vehicles, etc.), often already providing space for a few extra panels.
Another way to estimate is by power: every 1 kW in solar panels (approximately two 500 W plates) generate an average of 120 to 150 kWh/month (depending on location). So for every 100 kWh of consumption, you need approximately 0.8 kW of panels in the North or 1 kW of panels in the South, for example. So a consumption of 500 kWh/month could require a ~4 kWp system (about 8 500 W plates). These rules of thumb give an initial idea, but consult a specialist in solar energy for a detailed project is always recommended, ensuring that you invest in the right number of modules for your needs.
How long does a photovoltaic solar panel last?
Photovoltaic solar panels are known for their long service life. In general, the estimated useful life is 25 to 30 years and can last even longer than that. Most manufacturers offer 25-year performance guaranteeThis means that after 25 years the board should still be producing around 80% or more of its original power. In practice, this means that even after decades, the panel is still generating power, with only a slight annual degradation (typically ~0.5% per year in today's silicon modules).
A number of factors contribute to this durability: the boards are designed to withstand bad weather (rain, hail, strong wind, temperature variations). The front tempered glass protects against moderate impacts and the robust frame can withstand wind loads. In addition, the panels undergo laboratory tests (IEC standards) that simulate heat, cold, humidity and mechanical load cycles to ensure they can withstand severe conditions. With minimal maintenance and free of moving parts, no significant mechanical wearThe main effect is the slow degradation of the cell material and wear and tear of the encapsulants, something already taken into account in the guarantees.
Of course, in order to reach these 25+ years, the plate must be of good quality and that the installation is carried out properly. Installation faults (such as poorly crimped connectors, water infiltration due to improper drilling, etc.) can compromise longevity. However, by choosing certified equipment and qualified installers, you can expect your solar system to work for a long time. decades supplying energyThis is a great investment. It's worth remembering that many systems installed in the 1990s are still in operation today, and with technological developments, modern panels tend to be even more durable.
Does a solar panel need maintenance?
One of the great advantages of photovoltaic solar panels is the low maintenance requirements. Unlike combustion generators or other equipment, solar panels have no moving parts that are subject to constant wear and tear. Routine maintenance usually boils down to regular cleaning and occasional visual inspections.
Cleaning: In places with frequent rain, the rainwater itself helps to keep the panels clean by removing dust and light debris. However, in very dry regions or with excessive dust in the air, dirt or bird droppings can accumulate on the modules, which reduces generation. In such cases, careful cleaning of the glass surface is recommended every 6 months to 1 yearor as required. Cleaning can be done with water and a soft sponge or non-abrasive cloth, preferably in low sunlight (early morning or late afternoon) to avoid thermal shock on the hot glass. Never use strong chemical products or steel sponges, as they can damage the layers of the panel.
Inspection: It is useful to check from time to time if there is anything out of the ordinary - for example, check all connections are tightIt is also important to check that the cables are undamaged and that no new shadows have appeared on the panel (such as tree branches that have grown). Most systems operate without problems for years, but annual monitoring by the installer or O&M (Operation and Maintenance) professional can identify and prevent any loss of performance. It is also important to keep nearby trees pruned to avoid shading or excessive leaf fall on the modules.
Corrective maintenance: In the event of a breakdown or damage, such as an inverter that stops working or glass cracked by impact, specialist assistance should be called in. Cracked or delaminating boards usually need to be replaced to avoid compromising the system. Fortunately, such occurrences are rare. Inverters, cables and structures may require some maintenance over the decades (inverters usually have a lifespan of 15 years and may need to be replaced once during the life of the system), but the solar modules themselves require very little care in everyday life. This makes solar energy a very practical option: you install it and, as well as monitoring generation via the app or system, you practically "forget" it's there, except for the relief on your electricity bill!
How to choose the best solar panel?
Faced with so many options for brands and models of solar panels, it is important to consider certain criteria when making your choice, ensuring that you invest in quality equipment that is suitable for your project. Here are the main points to evaluate:
- Efficiency and Power: check the power (Wp) of the module and its percentage efficiency. Higher efficiency boards make better use of space, and higher power means fewer boards for the same total capacity. For example, if you can choose between a 450 W panel and a 550 W panel, the latter will require fewer units to achieve a given total power, as long as it physically fits on your roof.
- Tolerance and performance: many manufacturers provide a temperature coefficient (how much the power drops with increasing ambient temperature), lower coefficients indicate better performance in hot locations. Also, see if the panel performs well under low irradiance (cloudy days). Checking the technical specifications and comparing them can reveal which panel generates a little more in real conditions.
- Dimensions and weight: make sure that the panel fits into the available space and that the roof structure can support the weight. Some high-power models are physically larger (e.g. 2.2 meters high instead of 1.7 m). Panels with half-cut cells, on the other hand, may differ slightly in size. There are also "big cells" 210 mm, which tend to be larger. Choose a format that is compatible with your installation area.
- Manufacturer and warranty: opt for reputable manufacturersthat offer a guarantee of at least 10 or 12 years against defects manufacturing and 25 years of performance. This way, you have back-up in case the board fails prematurely. Reliable brands also adhere to international quality standards (IEC 61215, IEC 61730, ISO 9001, etc.) and generally offer better after-sales service. It's worth researching their reputation and service presence in Brazil.
- Price vs. quality: Evaluate the cost per watt of the options, but don't just go for the cheapest. Sometimes paying a little more for a higher efficiency panel or solid brand pays off in extra generation and peace of mind in the long run. Consider the cost-effectivenessincluding possible differences in performance between models.
- System compatibility: make sure that the panel's electrical specification (open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current) is compatible with your inverter and design. Normally, panels of the same category are similar, but if you are going to mix different models in a system, the designer must confirm compatibility. In new installations, it is customary to use all the same panels.
If in doubt, a good practice is consult specialized companies or integrators trustworthy. They can recommend models that they have had good experience with and that are suitable for you. At the end, the best solar panel will be the one that meets your energy consumption, physically fits your installation site and has quality assured to last for decades. Today, there are top-notch boards produced locally in Brazil, for example the BYD manufactures state-of-the-art modules in Campinas (SP), with TOPCon and half-cut technologies, achieving efficiencies of over 21% and guaranteeing up to 30 years performance. Looking for boards from manufacturers with domestic production can offer advantages in terms of support and warranty.
Examples of high-efficiency BYD solar panels
To illustrate, the BYD has a complete range of photovoltaic modulesThe BYD modules range from residential models to panels for large power plants. All BYD modules adhere to strict quality standards and come with a 12-year product warranty. linear power guarantee of 25 to 30 years (depending on the model). Below are some highlights of the BYD range and its features:
- BYD MLK-36 Monofacial 520-550 W: High-power monocrystalline panel, ideal for residential projects that need a lot of energy in a little space. It has an efficiency of ~21.3%, low annual degradation and can withstand high wind and snow loads. 25-year performance guarantee, ensuring at least 84.8% of power over that period. Great for residential roofs where you want to maximize generation with just a few units.
- BYD MGK-36 Monofacial 425-455 W: Lightweight monofacial module optimized for roof installations with weight or space restrictions. It has an efficiency of around 21%, a more compact design and is more lightfor easy handling. It stands out for its cost-effectivenessproviding excellent generation at an affordable price. Guarantees of 25 years, similar to the others.
- BYD HRP72S Monofacial 555-580 W: Very high power panel for homes with high consumption or commercial projects. It has an efficiency of up to 22.3% and excellent behavior at high temperatures (improved temperature coefficient). With power of up to 580 W per module, it reduces the number of panels needed in larger installations. It has 30-year linear warrantyThis means an extended service life and a greater return in the long term.
- BYD TUI66T Bifacial 595-620 W: N-Type TOPCon bifacial module with half-cell technology and transparent backsheet. First bifacial panel manufactured in Brazil with this technology. It achieves up to 22.7% efficiency and, because it uses light on both sides, it is perfect for plants and soil projects who want to extract every extra kWh. Lightweight and resistant, it comes with a 30-year warranty. Suitable for solar farms and ground applications with trackers for maximum production.
Each of these models caters for specific scenarios, but they all share BYD quality. By choosing a BYD solar panel, you invest in state-of-the-art technology and local supportYou can count on one of the world's leading manufacturers in the photovoltaic segment. This means high-efficiency panels, proven reliability and a solid guarantee, essential factors for the success of your solar project.
Why invest in solar panels today?

Installing photovoltaic solar panels has become one of the better economic and environmental decisions that you can take for your home or business. The main reasons for investing in solar energy today include:
- Saving on electricity bills: by generating your own energy, you drastically reduces monthly expenditure with electricity. In Brazil, energy tariffs have risen above inflation, and relying on the grid means facing constant increases and tariff flags. With a solar system, most of the energy consumed comes from the sun (which is free), and the electricity bill can drop by 50%, 80% or even zero, depending on the size. The initial investment pays for itself precisely in these savings: after the payback, you continue to enjoy energy at practically no cost.
- Financial return and property appreciation: Solar energy is not just an expense, it's a investment. The rate of return is usually higher than many financial investments, considering the savings generated. What's more, a property with a solar system tends to be increase in value on the real estate marketThis is because future buyers see the benefit of low electricity bills and energy independence. There is also the possibility of selling surpluses (energy credits) in some cases of shared generation, creating an indirect source of income.
- Sustainability and environmental responsibility: by opting for solar energy, you decreases your carbon footprint and contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Each solar kWh generated avoids burning fossil fuels or running polluting thermoelectric plants. In 2023, for example, Brazil experienced a major blackout and energy crises; solar systems with batteries helped to prevent this. keeping essential services running during blackoutsavoiding losses. In other words, as well as being sustainable, solar energy brings energy security at critical times, especially when combined with storage solutions.
- Independence and predictability: with your solar panels, you are less exposed to external variations, whether it's a rise in electricity tariffs or a lack of power on the grid. In on-grid systems, if the tariff goes up, your solar income goes up with it (you save more). And in hybrid systems with batteries, you can even keep equipment running during grid failures, guaranteeing power for your family or business 24 hours a day. Even without batteries, knowing that a large part of your energy comes from the sun makes your expenses more economical. predictable and protected from red flags or water shortages.
- Current facilities and incentives: It has never been easier to adopt solar energy. Costs have fallen by around 80% in the last decade, and today there are several specialized companies offering turn-key installation. Banks and financial institutions have specific credit lines for solar energy, with low interest rates and installments that are often pay for themselves with the savings in the account. In addition, the legal framework for distributed generation guarantees stable rules for those who install until 2045, including exemption from tariffs on compensated energy when the system is registered on time. In other words, those who invest now will secure regulatory benefits for decades to come.
In short, investing in solar panels today is ensure immediate and long-term savingswhile at the same time combining sustainability and innovation. With increasingly advanced technology and complete solar energy solutions available on the marketThis is the ideal time to use the sun's energy to your advantage.
If you want to be part of this energy revolution and start generating your own clean energy, get to know the high-efficiency BYD solar modules and reduce your electricity bill with solar energy right now. BYD offers complete solutions in panels, inverters and batteries for all project sizes, request a personalized quote here and take the next step towards energy independence!
Discover BYD solar modules and start generating your own clean energy right now!
Photovoltaic solar panels have established themselves as a reliable and affordable solution for generating electricity in homes, businesses and farms. In this guide, we look at what solar panels are, how they work and how they can turn sunlight into real savings on your electricity bill. We cover the various types and technologies, from traditional monocrystalline panels to the latest innovations, as well as practical questions about cost, expected generation, quantity needed, durability and minimum maintenance.
With clear information, it's clear that solar energy is a smart investment: as well as reducing costs and helping the environment, it increases the value of the property and brings energy independence. If you've made it this far, you've already taken the first step by getting informed. Now, how about bringing this technology into your everyday life?
Get in touch with solar energy specialists, tailor-make a project and start using the sun as your ally. A BYD Energy, a leader in photovoltaic solutions, is ready to help you on your journey, from state-of-the-art solar panels to full technical support. Find out how solar panels can change the way you consume energyThis guarantees savings and sustainability for many years to come. Invest in the energy future of your assets and reap the benefits now!
Frequently asked questions about solar panels
Do solar panels work on cloudy days or at night?
Yes, solar panels work on cloudy daysbut with reduced capacity. Even when the sun is not visible, there is diffused light that the photovoltaic cells can convert into energy, although generation falls (it can be between 10% and 50% of normal, depending on the density of the clouds). Now at nightThe plates do not generate electricity because there is no sunlight available. Therefore, at night the electricity consumed comes from the grid or from batteries, if the system has storage. It is important to remember that on-grid systems use energy from the grid automatically when there is no solar production (night or bad weather), so that the user is not left without light. Alternatively, those who want independence at night can invest in batteries to store the solar energy generated during the day and use it after sunset.
Will people with solar energy lose their electricity in the event of a grid blackout?
It depends on the type of system installed. In a common photovoltaic system connected to the grid (on-grid) without batteriesFor safety reasons, the inverter shuts down during a power cut in the grid. This is a mandatory standard to protect technicians who are repairing the grid, so even if it's daytime, if the grid goes down, the solar system also interrupts the supply. So if you only have on-grid solar panels unfortunately, the lights also go out during the blackout.
On the other hand, systems with batteries (backup) or generators can continue to supply energy during a grid outage. If you have a hybrid system (plates + batteries + hybrid inverter), when a blackout occurs the inverter disconnects from the grid but continues to power the house using the energy stored in the batteries. This way, essential items can continue to function normally.
This feature has become especially popular after blackout incidents: solar energy systems with batteries help avoid damage and inconvenience by keeping appliances on even when the utility fails. In short, to have light in the blackout with solar energy, you need to include storage or an off-grid scheme; otherwise, the standard on-grid system shuts down for safety reasons.
What is the difference between a photovoltaic solar panel and a thermal solar panel?
Although both are called "solar plates", they have different functions and purposes. A photovoltaic solar panels (the subject of this article) converts sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. The solar thermal panel (also called a solar collector) uses the sun's heat to heating water or other fluid. In other words, in solar photovoltaics the result is electricity to power light bulbs, household appliances, etc., while in solar thermal the result is heated water for bathing, swimming pools or industrial uses.
Solar thermal panels are usually metal or glass panels with internal pipes where water circulates and is heated by the sun. They do not generate electricity but heat. They are widely used in solar water heating systems in homes, reducing the need for electric showers or gas boilers. Photovoltaic panels, on the other hand, produce electricity that can power any electrical load, including possibly an electric boiler, but they do not heat water directly.
In a nutshell: photovoltaic panels = electricity, thermal plates = thermal energy (heat). Both harness the sun and can coexist in a house (for example, photovoltaic panels on the roof for electricity and a solar collector for shower water). It's important not to confuse them when planning your solar energy project, as each requires different equipment and installations.
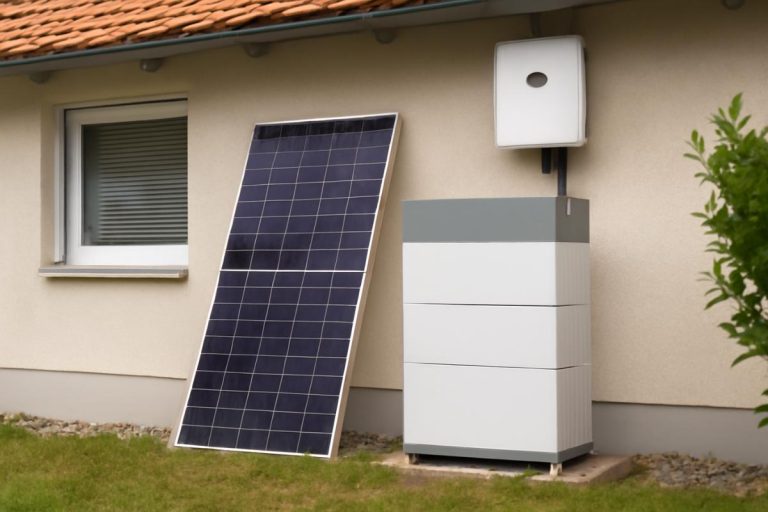
Do I need batteries to harness solar energy in my home?
Not necessarily. The vast majority of residential solar energy systems in Brazil are connected to the electricity grid (grid-tie) and no batteriesThe solar panels work on an energy compensation scheme with the utility company. In this model, during the day the panels generate energy and supply the home's consumption; any surplus goes into the grid, generating credits that are used at night or during sunless periods. This arrangement avoids the cost of batteries and still provides maximum savings on the electricity bill.
However, there are situations in which batteries can be recommendedFor example, if you want to have energy backup in case of power outages (as explained above), or if the system is completely isolated from the grid (off-grid), such as in remote rural areas. In these cases, batteries store the electricity generated by the plates during the day for use at night or in emergencies. Today there are modern lithium batteries, such as the lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4)which offer a long service life (more than 10 years) and high charging/discharging efficiency - technology that is also used in the BYD batteries residential and commercial storage.
Therefore, for the average user connected to the grid, batteries are optional and seen more as an additional feature to greater autonomy. It's perfectly possible to use solar energy in your home without any batteries, saving money on your electricity bill via the distributor's credit system. But if you're looking for total independence from the grid or backup against blackouts, integrating a battery system is the way to go. Evaluate the cost-benefit: batteries increase the initial investment, but they add security and can meet specific needs (such as keeping refrigerators, medical or IT equipment running in a blackout). Fortunately, the market already has complete solutions for energy storage integrated with photovoltaic systems, which used to be rare, is now a growing reality.








